
|
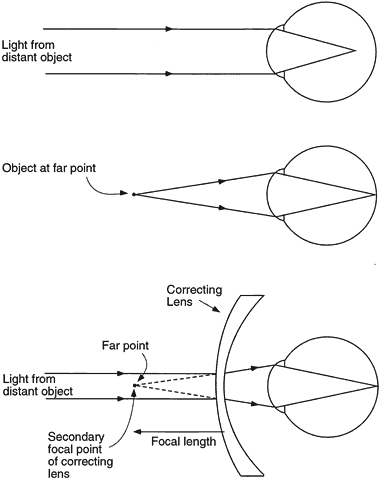
| Fig. 1. Optical correction of myopia. Light from a distant object focuses in front of the retina of the uncorrected eye. For the image to fall on the retina, the object must be placed at the far point of the eye. Alternatively, a minus-power correcting lens may be placed in front of the eye to provide divergent light that simulates light coming from a near object. The secondary focal point of the correcting lens falls at the far point of the eye. |