

|
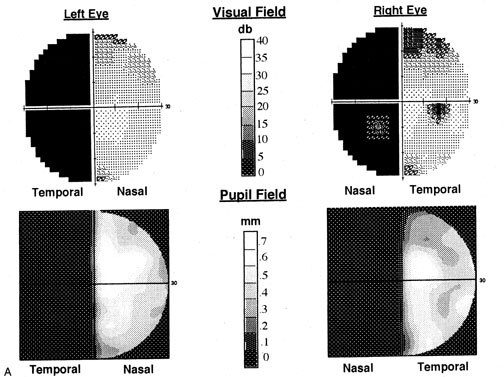
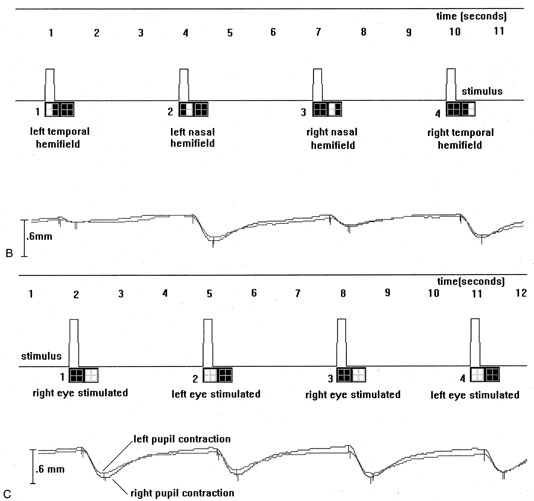
| Fig. 3. Pupil perimetry results in optic tract lesions. A patient with a right optic tract lesion has incongruous left homonymous hemianopia (A, top) and lacks pupillary responses to focused light in the blind hemifield (A, bottom). This is also shown with hemifield light stimulation (B), where light in the left eye's temporal hemifield (pulse 1) and the right eye's nasal hemifield (pulse 3) elicits much less pupilloconstriction than light in the seeing hemifields (pulses 2 and 4). In addition, pupillometry with full-field stimuli (C) shows smaller amplitudes of pupil constriction to light in the left eye (pulses 2 and 4) than in the right eye (pulses 1 and 3), confirming a left RAPD. (Courtesy of Dr. R. Kardon, University of Iowa.) |