|
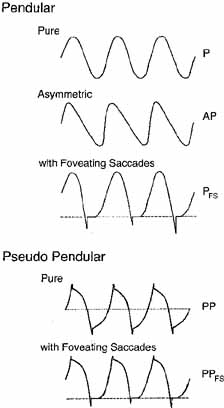
Fig. 4 Variations of
pendular nystagmus due to pursuit-system instability: pure (P), asymmetric
(AP), pendular with foveating saccades (PFS), pseudopendular
(PP), and pseudopendular with foveating saccades (PPFS). Note
that although foveating saccades vary in amplitude, all achieve foveation
(i.e., they all return the eyes to same point, the target). Foveation takes
place at the peaks that are more flattened; here shown as the leftmost peaks.
In this and Figures
5, 6, 7
and Figure 16,
dashed lines indicate target position (see text). In all figures, upward
deflections indicate rightward, upward, or clockwise eye movement (all eye
movements are from the patient's perspective). |