
|
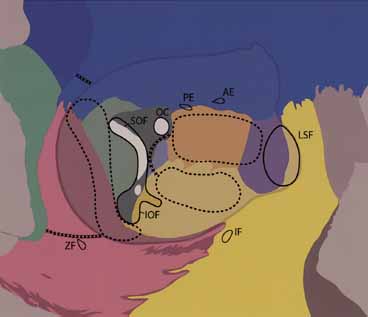
| Fig. 6 Orbital bony anatomy: frontal bone (blue); greater wing of sphenoid (light green); lesser wing of sphenoid (dark green); zygoma (pink); maxilla (yellow); lacrimal bone (purple); ethmoid bone (orange); palatine bone (pale blue). AE=anterior ethmoidal foramina; PE=posterior ethmoidal foramina; OC=optic canal; SOF=superior orbital fissure; IOF=inferior orbital fissure; LSF=lacrimal sac fossa; IF=infraorbital foramen; ZF=zygomaticofacial foramen. Dotted lines demarcate deep lateral wall removal (which includes the greater wing of sphenoid from the edge of the SOF to IOF), areas of medial wall, and floor removal. The entire lateral orbital call can be removed (x-line) and advanced with a vulgus rotation. Removal of medial wall should not extend above the anterior and posterior ethmoidal foramina, which denote the level of the cribriform plate. When the floor and medial wall are removed, a strut of bone as depicted can be left to minimize postoperative ocular motility problems. Very little additional decompression is obtained by removal of the floor lateral to the infraorbital groove. For maximal apical decompression, palatine bone can be removed up to the optic canal (x-line). |