
|
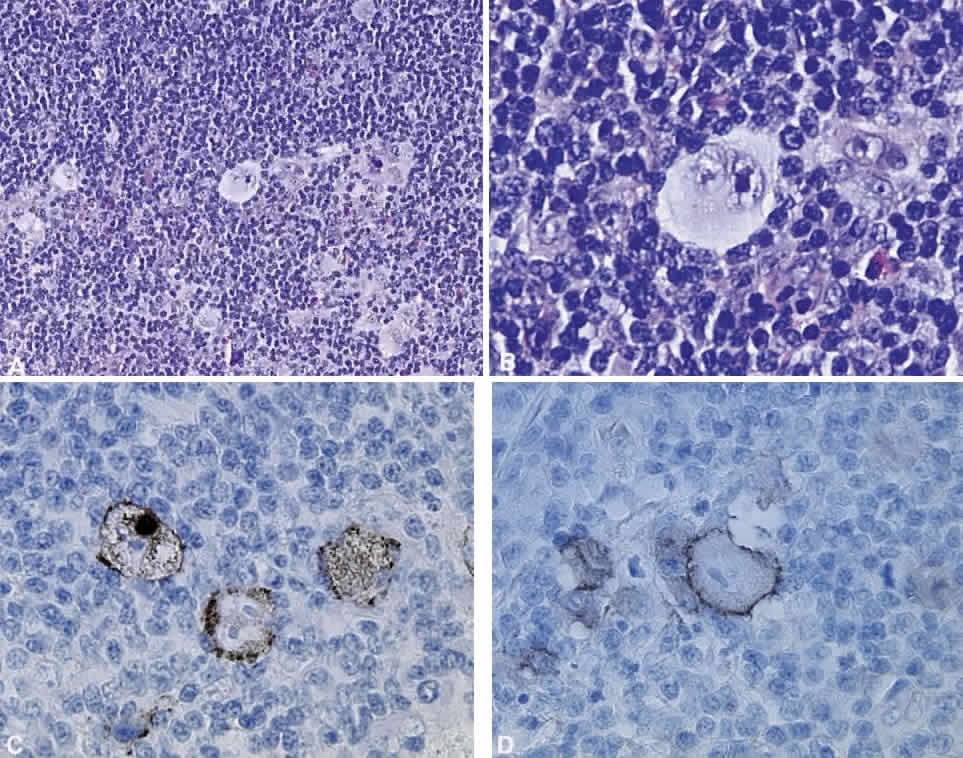
| Fig. 20. Hodgkin's disease. A. A typical infiltrate of small lymphocytes, scattered eosinophils, and occasional large Hodgkin's cells (hematoxylin and eosin, × 20). The Hodgkin's cell, Reed-Sternberg type, which has a bilobed nucleus with prominent basophilic nuclei. B. A collar of small lymphocytes intimately surrounds the cell and an eosinophil is visible to the right of the Reed-Sternberg cell (hematoxylin and eosin, × 60). C. Hodgkin's cells demonstrated by CD15 staining (immunoperoxidase, × 60). D. Hodgkin's cells demonstrated by CD30 immunohistochemical study (immunoperoxidase, × 60). (Courtesy of Dr. A. Mowat) |