
|
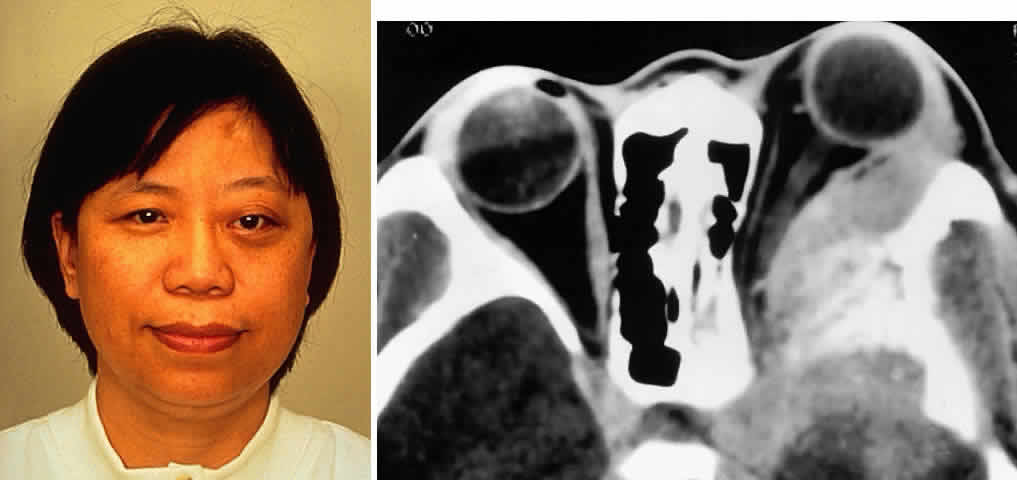
| Fig. 5. A 48-year-old Chinese woman had undergone previous frontotemporal craniotomy and partial excision of a left sphenoid wing meningioma. She presented 6 years later with progressive proptosis, visual loss, and numbness of the left cheek and upper teeth that developed during the preceding 2 years. On external examination, she had fullness of the temporalis fossa, an axial proptosis of 11 mm, and downward displacement of the left globe 2 mm (A). Ocular ductions were moderately restricted in all fields of gaze. She had no light perception, marked optic disc pallor, and an optociliary shunt vessel. CT scan revealed an extensive regrowth of meningioma involving the sphenoid wing, with soft tissue components in the temporalis and middle cranial fossae, parasellar region, and orbit, shown here on axial view (B). The lesion also involved the cavernous sinus and pterygopalatine fossa. She underwent a combined resection via the frontotemporal orbitozygomatic approach, followed by radiotherapy (50 Gy in 25 fractions over 5 weeks) for residual components in the cavernous and sphenoid sinuses. Two years after surgery, she remains comfortable and without radiographic evidence of tumor regrowth. Proptosis was reduced to 1 mm axially. |