
|
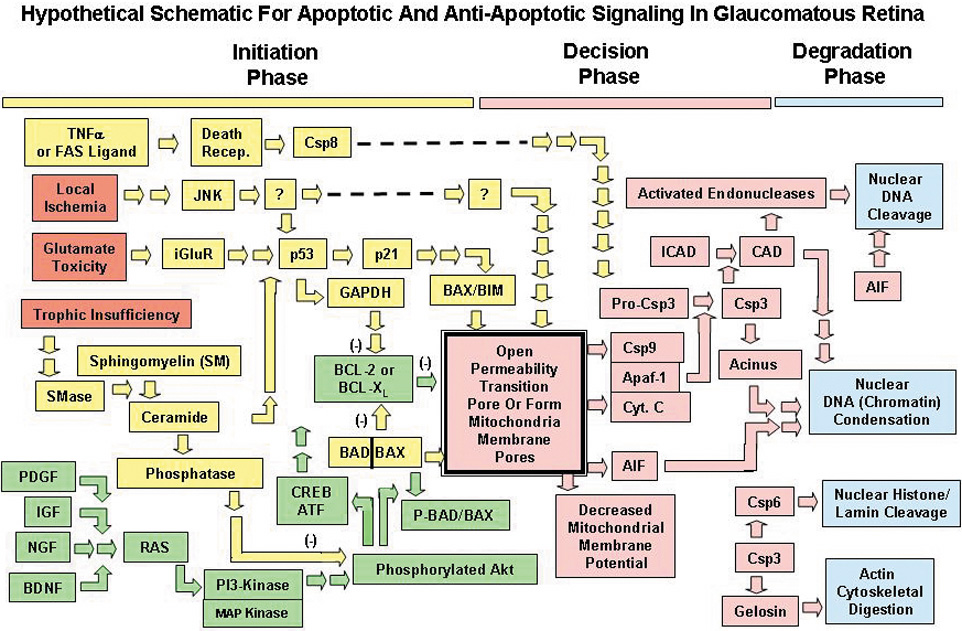
| Fig. 1. Three phases for hypothetic pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic signaling in retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) of a glaucomatous retina. The initiation phase (yellow bar at top) includes the three insults (focal ischemia, glutamate excitotoxicity, trophic insufficiency) thought to be most involved in RGC death (red). Initiation phase: pro-apoptotic pathways/proteins (yellow), antiapoptotic pathways/proteins (green). The next decisional phase (pink bar at top); the final degradation phase (blue bar). Cytochrome C (Cyt. C) plus apoptosis-activating factor (Apaf-1) plus Csp9 (caspase-9) are shown blocked together as they complex to form the apoptosome. TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor alpha; SMase, sphingomyelin hydrolase; PDGF, platelet-derived growth factor; IGF, insulin-like growth factor; BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; iGluR, inotropic glutamate receptors; JNK, p53, and RAS are transcription factors; Csp (3, 6, 8, 9) are caspase proteases; Akt, protein kinase B; PI3-k, phosphatidyl inositol-3-kinase; MAPkinase, mitogen activated protein kinase; CREB-ATF, cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element binder–activated transcription factor; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase; BCL-2, BCL-XL, BAD, BIM, and BAX are members of the BCL-protein family; P-BAD, phosphorylated BAD; CAD, Csp-3–activated DNA-se; ICAD, inhibitor of CAD; Acinus, Csp-3–activated protein mediating chromatin condensation; gelosin, cytoskeletal protein protease. (Modified from Tatton WG, Chalmers-Redman RME, Tatton NA: Apoptosis and antiapoptosis signaling in glaucomatous retinopathy. Eur J Ophthalmol 11(Suppl 2):S12, 2001.) |