
|
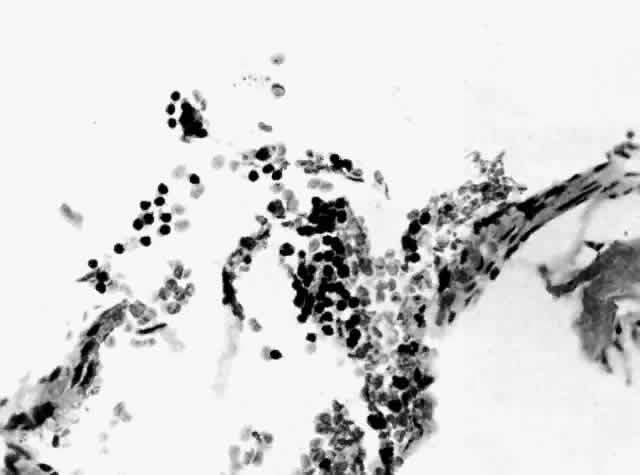
| Fig. 18. A nonrhegmatogenous retinal detachment associated with a ciliochoroidal effusion in a 46-year-old man. A ciliary body biopsy, performed because a ring melanoma was suspected, showed a mild lymphocytic infiltrate. Similar changes developed in the fellow eye, and the patient was considered to have uveal effusion syndrome. Exhaustive studies gave no clues to the etiology. The cerebrospinal fluid protein was slightly elevated. During a 10-year period, the patient's vision decreased to count fingers (H & E, × 440). (Courtesy of the Armed Forces Institute of Pathology, Washington, DC) |