
|
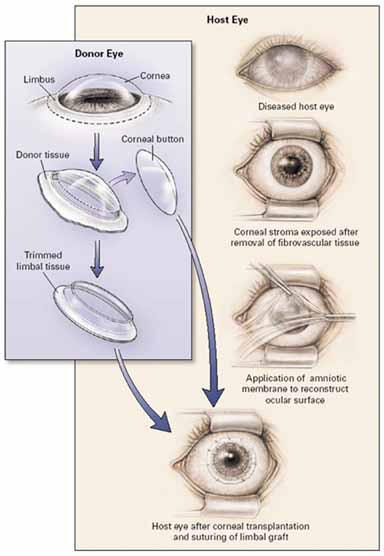
| Fig. 10 Surgical procedure of keratolimbal allograft (KLAL). In the host eye the fibrovascular pannus is completely removed leaving in most of the limbal stem cell deficiency (LSCD) cases a clear residual corneal stromal bed. One layer of amniotic membrane with basal membrane up is place over the cornea as a graft and secure with interrupted 8-0 vicryl to residual conjunctiva and scleral tissue around the limbus. The donor central corneal button is removed by trephine and the residual limbal ring is trimmed off and the underlying stroma is thinned to create a smooth and thin corneal–scleral limbal ring. The limbal tissue is then lay around cornea and secure with interrupted 10-0 nylon suture. In order to promote corneal epithelial healing another amniotic membrane is placed over the cornea as a patch and secure to the scleral with running 10-0 nylon for 1 or 2 weeks (figure not shown). If amniotic membrane is dissolved before 2 weeks, exposure and/or severe inflammation should be suspected and addressed. (Reprinted from Tsubota K, Satake Y, Kaido M, et al: Treatment of severe ocular surface disorders with corneal epithelial stem-cell transplantation. N Engl J Med 340:1697, 1999, with permission) |