
|
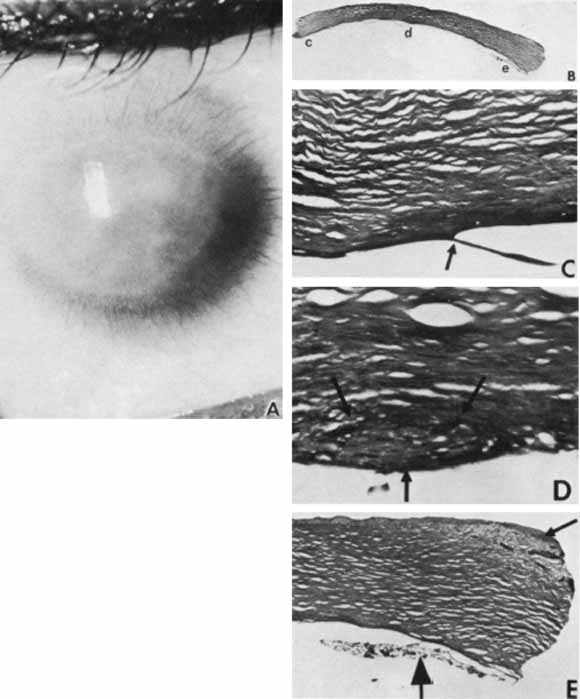
| Fig. 20 Peters anomaly. A. There is superior and inferior scleralization of the cornea and a central corneal opacity that extends to the periphery everywhere except the 3 to 5 o'clock meridian. B. Keratoplasty button demonstrates thick peripheral Descemet's membrane (c), central absence of Descemet's membrane and endothelium (d), and iridocorneal adhesions (e) (PAS, ×4). C. Peripheral Descemet's membrane is thick, multilaminar, and split (arrow). It gradually disappears more centrally. D. Within the central posterior corneal defect is a fusiform fibrous plaque (arrows) (PAS, ×256) E. Iridocorneal adhesion is present at the edge of the posterior corneal defect (large arrow). Superficial subepithelial fibrous tissue and vascularization represent the central extension of the sclerization (small arrow) (PAS, ×64). (A–E reproduced from Waring GO, Rodrigues MM, Laibson PR: Anterior chamber cleavage syndrome. Surv Ophthalmol 20:3–27, 1975) |