
|
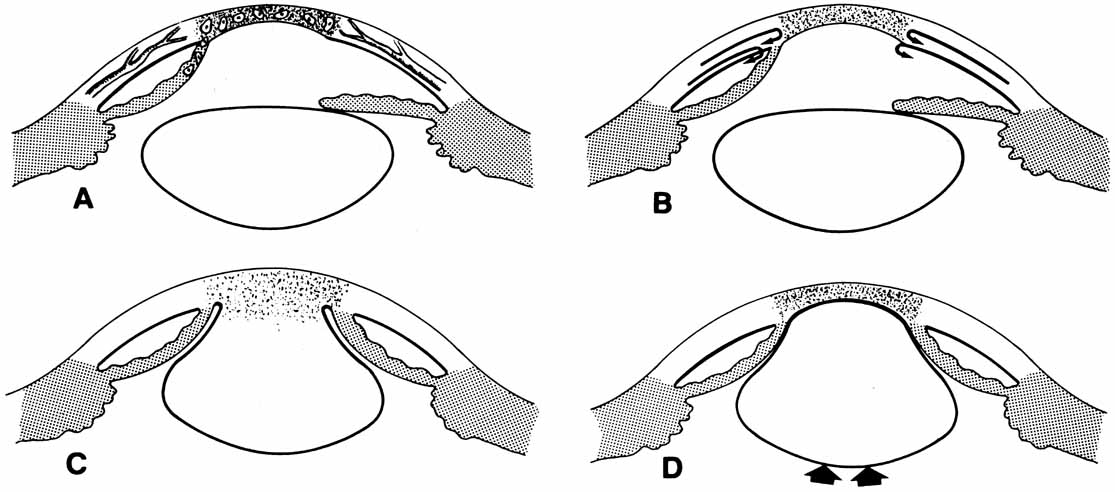
| Fig. 24 Four possible mechanisms for the formation of congenital posterior corneal defects. A. Intrauterine inflammation. B. Incomplete central mesenchymal migration. C. Improper lens vesicle separation from surface ectoderm. D. Anterior lens displacement by vitreoretinal mass. |