
|
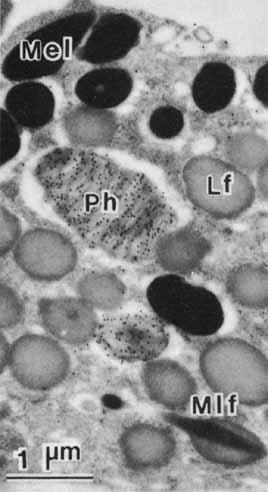
| Fig. 15 Immunocytochemistry, using monoclonal antibodies to a nine amino acid fragment at the carboxy terminus of rhodopsin, demonstrates opsin in a large phagosome and, more basally, in a small phagolysosome (Ph) or secondary lysosome. No lipofuscin granules (Lf) react, indicating the absence of the carboxy terminal region of the rhodopsin molecule. In the preparation of this specimen, osmic acid was not used as a fixative and “electron stain”; therefore, the lipids in the cell were extracted by solvents employed for dehydration of the tissue and lipoidal components of the cell (e.g., membranes, lipofuscin) have no electron density. By contrast, melanin has native electron density (×15,000) (Mel, melanosome; Mlf, melanolipofuscin). (Feeney-Burns L, Gao C-L, Berman ER: The fate of immunoreactive opsin following phagocytosis by pigment epithelium in human and monkey retinas. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 29:708, 1988) |