
|
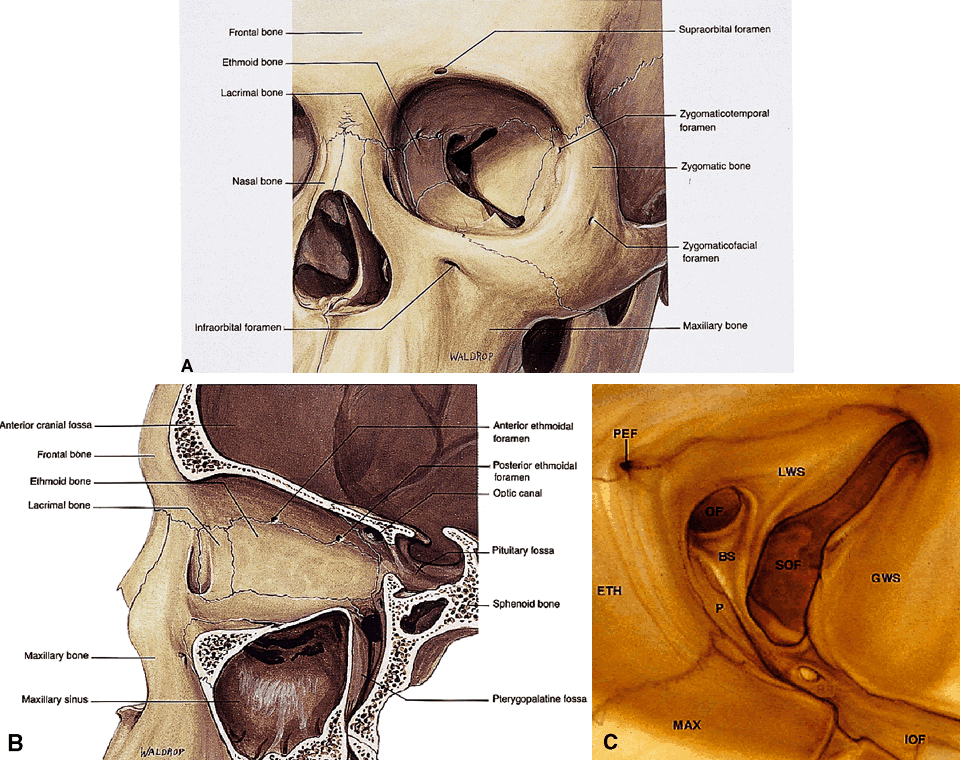
| Fig. 7. Orbital osteology. A. Oblique frontal view. Note that the supraorbital foramen and infraorbital foramen usually lie in the same vertical plane. The supraorbital foramen may also occur as a notch. Note the discontinuity of the orbital rim medially, forming the lacrimal sac fossa. B. Parasagittal view. The largest diameter of the orbit occurs about 1 cm posterior to the orbital rim. Note the medial location of the optic foramen. The superior orbital fissure and CS lie in the same plane in the orbital apex. Note the vertical orientation of the pterygopalatine fossa located directly behind the maxillary sinus and communicating with the orbit through the inferior orbital fissure. C. Osteology of the orbital apex. GWS, greater wing of sphenoid; LWS, lesser wing; BS, body of sphenoid; P, palatine bone; MAX, maxillary bone; OF, optical foramen; SOF, superior orbital fissure; PEF, posterior ethmoidal foramen. (A and B modified from Dutton JJ: Atlas of Clinical and Surgical Orbital Anatomy, p 8. Philadelphia, WB Saunders, 1994. C modified from Zide BM, Jelks GW: Surgical Anatomy of the Orbit, p 8. New York, Raven Press, 1985) |