
|
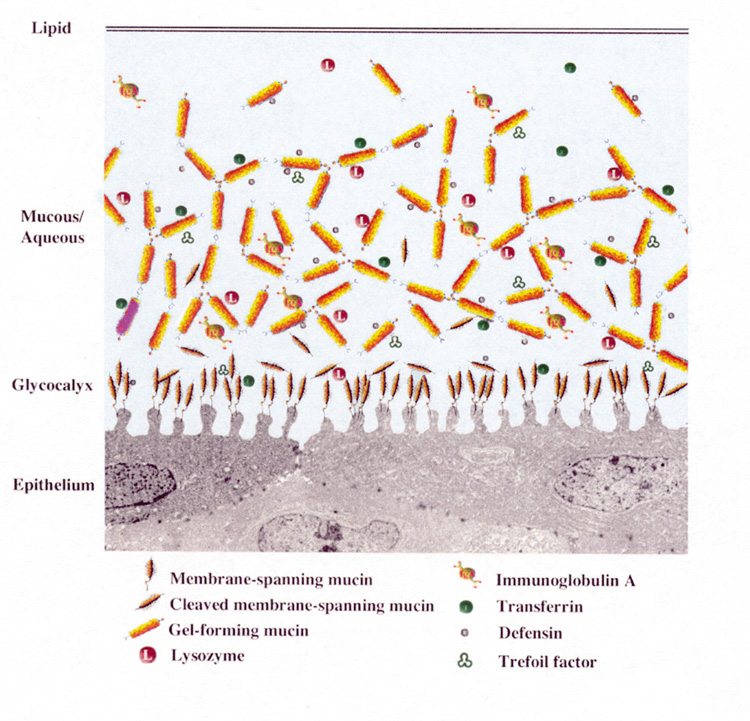
| Fig. 1. Diagram of the tear film hydrated gel. Membrane-associated mucins on the microplicae of the epithelium form the glycocalyx. Secretory mucins admix with the aqueous layer containing antimicrobial factors, such as lysozyme, and immunoglobulins secreted by the lacrimal gland. The anterior lipid layer provides stability by interacting with the mucin-aqueous phase, and is itself composed of polar and nonpolar phases. (From Gipson IK, Argueso P. The role of mucins in the function of the corneal and conjunctival epithelia. Int Rev Cytol 231:1-49, 2003, with permission.) |