
|
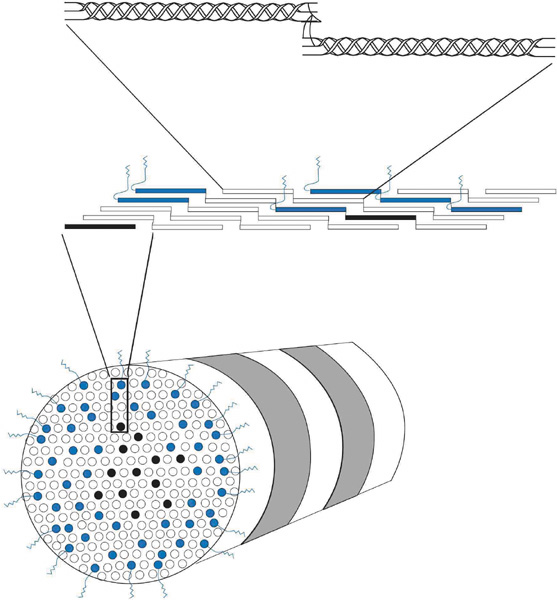
| Fig. 9. Cross-sectional oblique view of a 25-nm diameter, heterotypic, banded (periodicity = 68 nm) corneal stromal collagen fibril (bottom) composed of type I (white), III (black), and V (blue) collagen molecules. The amino-terminal domains on the type V collagen molecules appear to be important in regulating collagen fibril diameter as they project external to the fibril surface and presumably block further accretion of collagen molecules through steric and/or electrostatic hindrance effects. Notice that the collagen molecules on longitudinal view (middle) are aligned in a parallel, quarter-staggered (68 nm) arrangement with 40 nm gaps between molecules. Also, note that the longitudinal view (top) shows clearly that the ends of the alpha chains in each collagen molecules form intermolecular cross-links with adjacent collagen molecules. |