
|
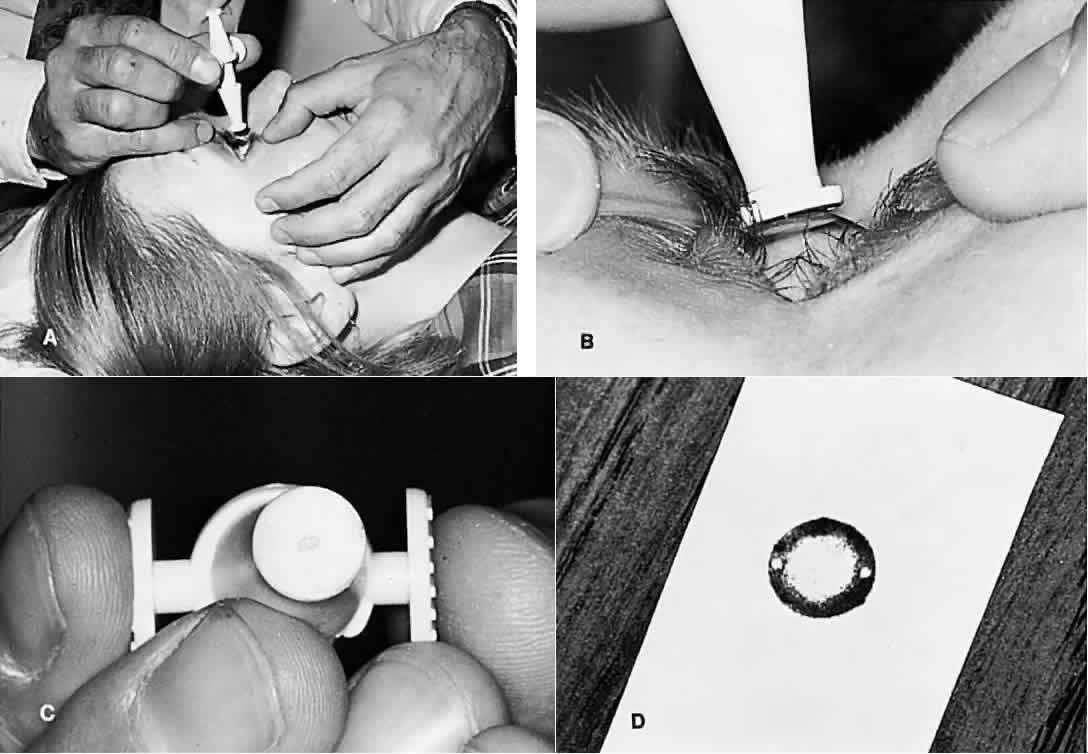
| Fig. 6. Posner-Inglima fixed-force applanation tonometer. (A) This tonometer is lowered onto the eye. (B) The cornea is flattened by the fixed weight of the plastic instrument. (C) The area of flattening is seen on the footplate as the light central portion where the ink originally smeared on the footplate has transferred to the flattened cornea. (D) The footplate is then pressed onto a sheet of paper. The remaining ink is transferred to the paper. The diameter of the flattened area can be measured from the clear central portion. The diameter can then be used to calculate the area applanated and the intraocular pressure. In actual use, the instrument is supplied with a scale that allows reading of the intraocular pressure directly from the diameter. |