
|
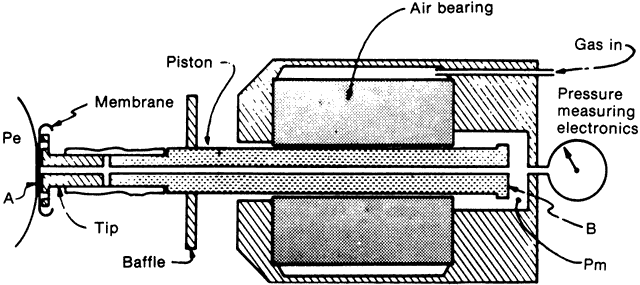
| Fig. 16. Schematic drawing of pneumotonometer plunger. The plunger (B) is pushed forward by gas pressure and rides on an air bearing. When the cornea (A) is flattened, so is the membrane on the tip of the plunger. The pressure in the tip then equals the intraocular pressure, and that pressure is transmitted to the area indicated by Pm, sensed and electronically displayed. Pe, pressure in eye (i.e., intraocular pressure). (West C, Capella JA, Kaufman H: Measurement of intraocular pressure with pneumatic applanation tonometer. Am J Ophthalmol 74:507, 1972.) |