
|
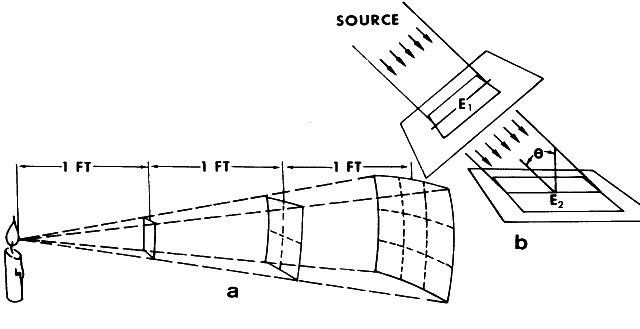
| Fig. 4. A. The inverse square law, which states that the amount of light continually diverges as one moves away from the source, thereby covering a greater area with lower intensity the greater the distance from the source. B. Lambert's cosine law: parallel rays of light falling on a plane surface will illuminate this surface directly in proportion to the cosine of the angle as measured normal to the irradiated surface. (Modified from Kaufman JE, Christensen JF [eds]: I.E.S. Lighting Handbook, 5th ed. New York, Illuminating Engineering Society, 1972) |