
|
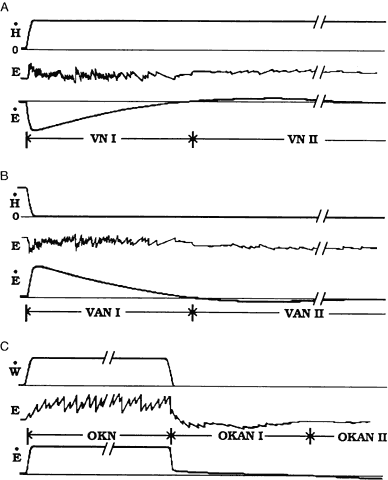
| Fig. 26. Continuous vestibular ocular reflex and optokinetic nystagmus. Per-rotatory nystagmus (A): continuous head rotation at constant velocity (H) begins from rest and elicits vestibular nystagmus. During the initial response phase (VN I) slow phase velocity jumps quickly to a compensatory level but decays to 0 in 20 to 30 seconds. In some patients, VN I is followed by a small-amplitude anticompensatory nystagmus that builds and subsides with a few minutes. Postrotatory nystagmus (B): Vestibular after-nystagmus elicited when rotation is terminated, mirrors the response in A. Optokinetic nystagmus (C): Continuous rotation of the visual world elicits enduring optokinetic nystagmus (OKN) for as long stimulation lasts. When lights are extinguished, a small-amplitude optokinetic after-nystagmus (OKAN I) continues in some subjects which may reverse direction (OKAN II). (Redrawn from Shupert C, Fuchs AF: Vision Res 28:585, 1988.) |