
|
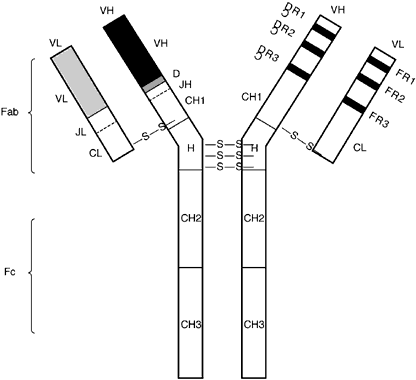
| Fig. 4. The immunoglobulin G molecule. The molecule is composed of two heavy-chain and two light-chain polypeptides joined by disulfide bonds (-S-S-) at the hinge (H) region. Both the heavy (H) and light (L) chains are composed of variable (V) regions at the N-terminus [the F(ab) fragment] and constant (C region domains at the C-terminus (one C region domain for the L chain, three C region domains for the H chain). The VH, CH, and CL region domains are depicted on one side of the F(ab) fragment, and the complementary determining regions (CDR) and framework (FR) areas on the other side of the F(ab) fragment. The FR regions are relatively conserved amino acid sequences of the variable regions that are interspersed among three highly variable regions called CDR. These hypervariable regions of the H and L chains interact to form a 3D structure, which constitutes the antigen-binding region. (After Medical Knowledge Self-Assessment Program [MKSAP]: Allergy and Immunology, Book 1, p 153. Philadelphia: American College of Physicians, 1993.) |