
|
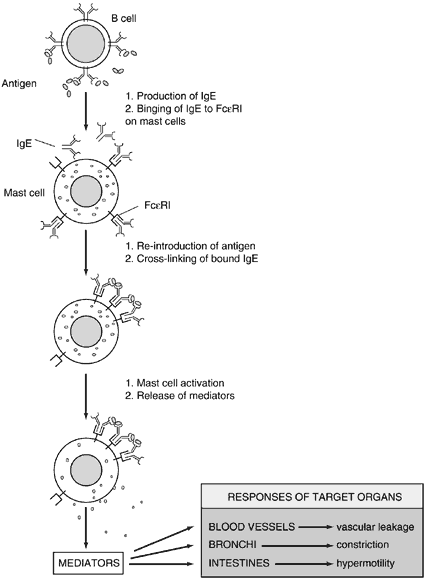
| Fig. 10. Sequence of events in immediate hypersensitivity. The initial contact with an antigen leads to specific immunoglobulin E (IgE) synthesis by B cells. Secreted IgE binds to mast cells or basophils through high-affinity Fcε receptors (FcεRI). On subsequent exposure to antigen, an immediate hypersensitivity reaction is triggered by cross-linking the IgE molecules. (After Abbas AK, Lichtman AH, Pober JS. Cellular and Molecular Immunology, p 296. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders, 1994.) |