
|
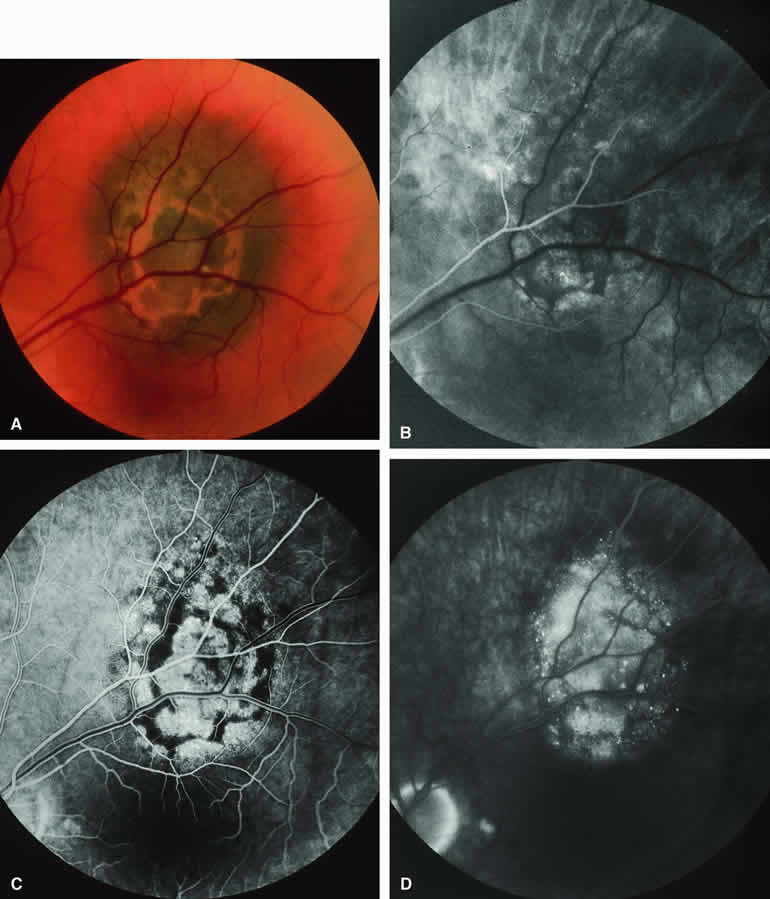
| Fig. 6. Melanotic choroidal nevus versus melanoma with prominent clumps of overlying orange pigment. A. Darkly melanotic choroidal lesion with prominent clumps of overlying orange pigment (lipofuscin). B-D. Fluorescein angiogram of lesion. B. Arterial phase frame showing irregular hypofluorescence and hyperfluorescence corresponding to lesion. C. Laminar venous phase frame showing generalized window defect hyperfluorescence of mass plus intense choroidal fluorescence blockage by orange pigment. D. Late-phase frame showing multiple pinpoint foci of hyperfluorescence at retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) level, leakage of fluorescein into the overlying and surrounding subretinal fluid, and partial obscuration of the blockage of choroidal hypofluorescence corresponding to the orange pigment on the surface of the lesion. |