
|
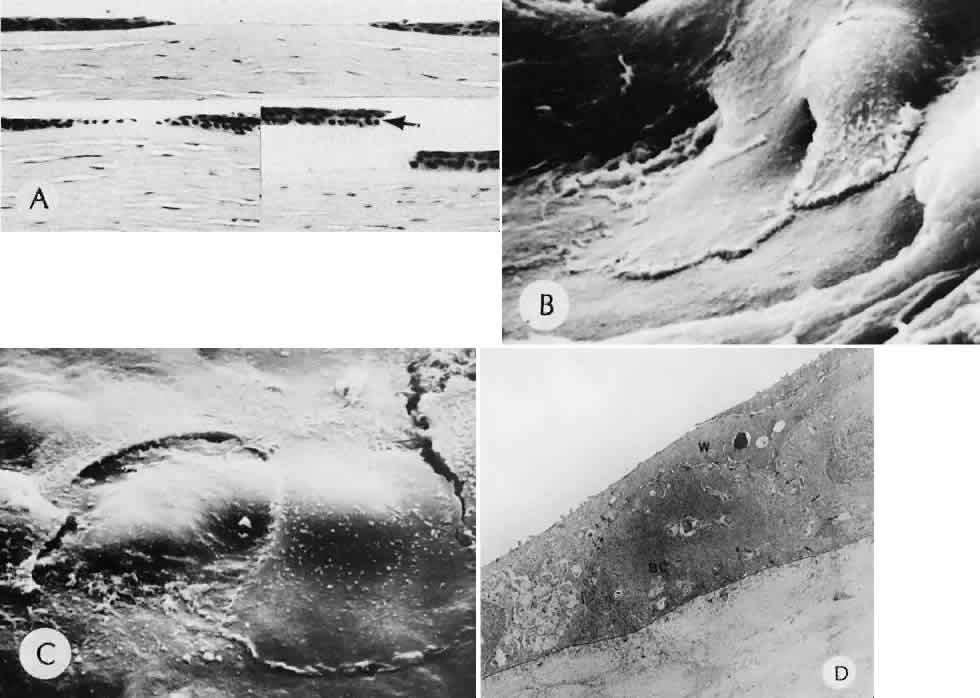
| Fig. 2. Corneal epithelial cell healing of an abrasion. A. Early in the repair process, epithelial cell layer attenuation is present at the edges of the abrasion (top). The epithelial wound heals by epithelial migration over Bowman's membrane (lower left). Artifactual epithelial breaks have right angle contours (lower right, arrows). (Hematoxylin-eosin stain; × 136.) B. Scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of the leading edge of the corneal epithelium 1 hour after mechanical abrasion. C. SEM of the leading edge of the migrating epithelium. Superficial cells not directly involved in migration may be desquamated. D. Transmission electron micrograph of the leading edge of migrating corneal epithelium 2 hours after mechanical abrasion. Desmosomes are continuous with the wing (W) cell layer overlying a rounded basal cell (BC). Note the loss of hemidesmosomes and the many lateral desmosomes (arrows) between the adjacent basal cells. There are few apical desmosomes between the basal cell on the right and the adjacent wing cell. (B—D: rabbit; × 4000.) |